Just about every security vendor has researched, blogged, and webcasted about how their product can and will prevent ransomware. Additionally, in my conversations with the security community, people always ask me: “What is the best product to prevent ransomware?” If you have read my Security Architect Lessons post, you know by now that I am not a fan of a single product to solve all the problems. Generally when I am asked how to prevent ransomware, my response is exploratory and factual, providing some of the best defense-in-depth methods that may be implemented today with ease and near zero business impact.
Your strategy to defend against ransomware needs to go beyond the standard backups and “up-to-date” anti-virus definitions. A defense-in-depth, holistic security program is required to prevent ransomware, and more importantly to detect it. This is by no means the only threat to your organization, therefore your focus should be on reducing your attack surface to prevent or detect threats in general. Having multiple layers in place with appropriate monitoring and alerting at each stage of the kill chain is critical to detection and prevention.
Whether you have dealt with ransomware or are preparing for it, I will guide you through practical techniques and technical controls that can help you to detect and prevent ransomware.
First, gauge your organization’s prevention appetite.
Every organization has a limit to the amount of prevention they are willing to accept. This is based on a few factors and should be considered before attempting to implement certain preventative controls. No single preventative product will stop all the different variations of ransomware or specific types of threats. Every associate or department has different needs. Development teams require specialized applications and services that, if interrupted, can prevent a product from completion. Accounting and HR departments open spreadsheets and documents that require macros. IT and security teams are there to support users, and prevention tools can get in the way. Executive leadership teams sometimes do not have time for a 15-character password or 5-minute screensaver lock. How much is too much? Are we preventing threats or preventing the organization from being successful?

Our goal is to make the attacker’s job hard. Before implementing controls, ask yourself:
- What amount of prevention is acceptable in my business?
- Are there certain parts of my organization that can have more prevention versus others?
- If I cannot prevent it, can I detect it?
- Where do I have visibility gaps? (Systems off network, off domain, Linux/Mac)
Resources for Getting Started
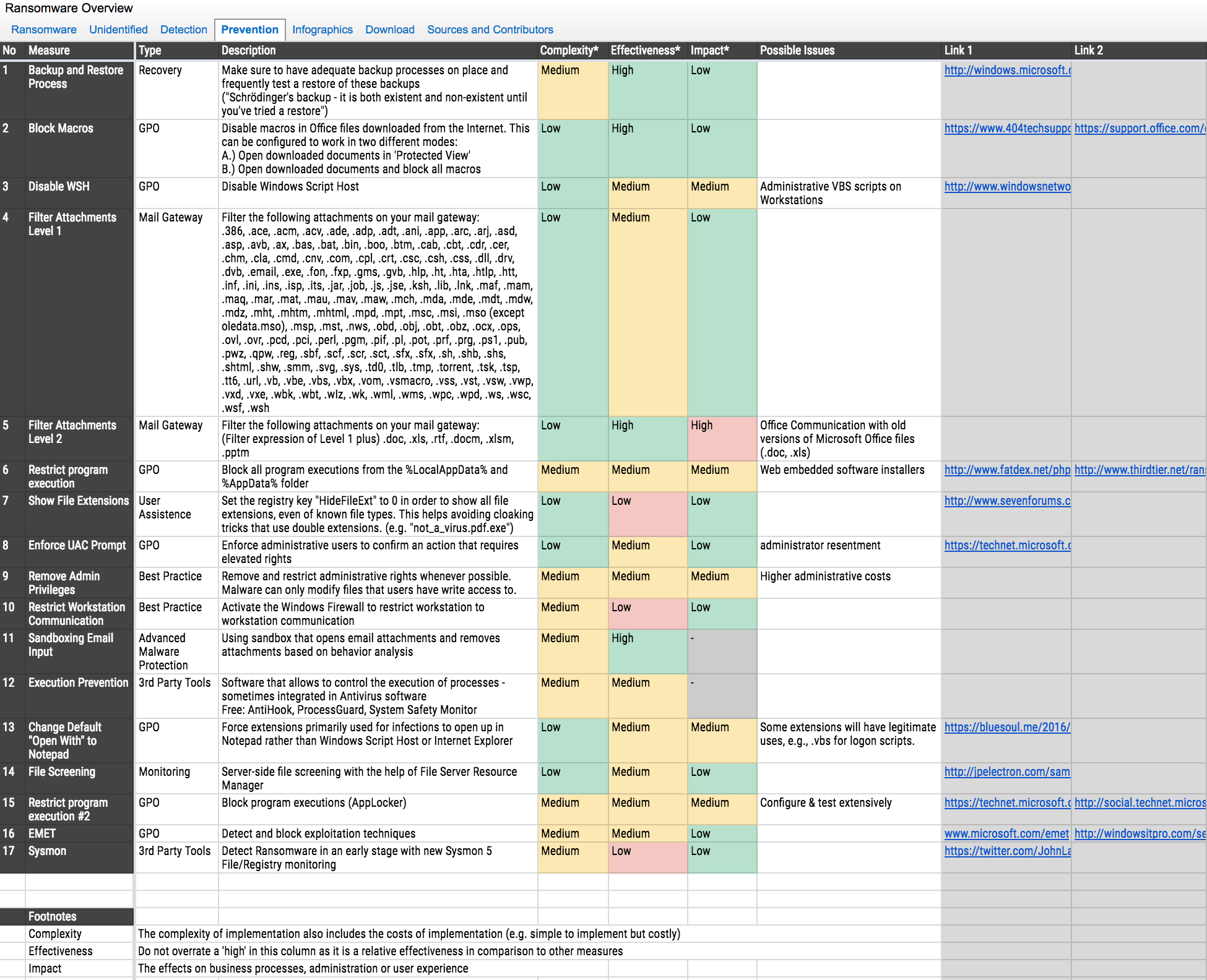
During our recent webinar on the ransomware epidemic, I referenced 17 different ways to assist with preventing ransomware. This list was generated by many contributors in the industry who, just like us, are battling ransomware. These techniques all play a part in your defense-in-depth program. I highly recommend reviewing the following spreadsheet and impact matrix to make a decision on what next steps may be best for your organization.
Ransomware Overview Spreadsheet
This spreadsheet was compiled by Florian Roth, a leading information security contributor. He works with a number of other expert contributors across various organizations to keep it up-to-date:
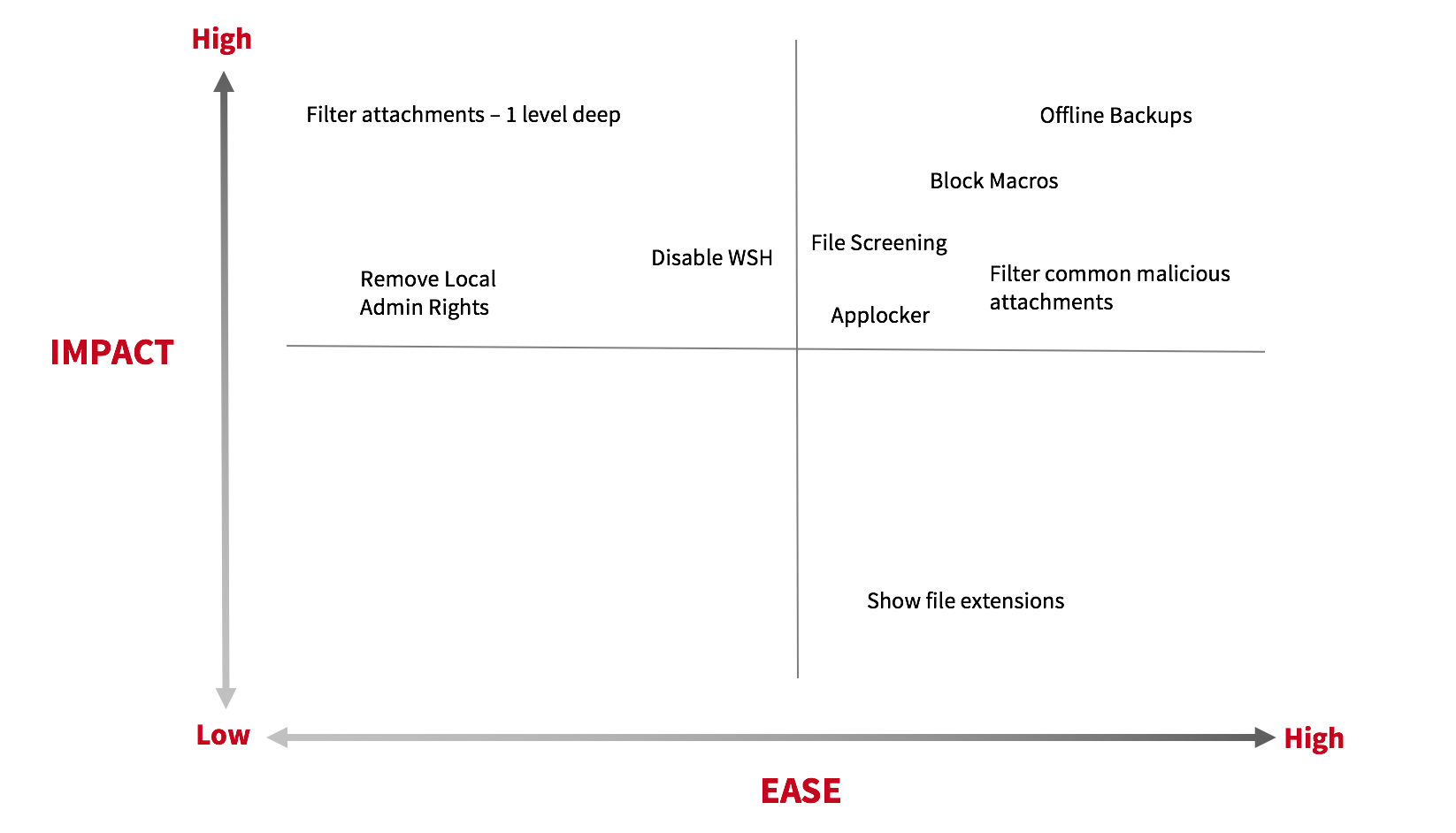
 Impact Matrix
Impact Matrix
I generated a simple impact matrix of countermeasures I thought to be the most impactful based on the spreadsheet outlined above. As you review this matrix, take into consideration other tools and their effectiveness today in preventing/detecting threats. Build a custom matrix based on your organization’s environment.
 5 Countermeasures & Technical Controls
5 Countermeasures & Technical Controls
1: Use Microsoft Applocker to block extension types.
In speaking with many organizations about the use of the built-in Microsoft Applocker utility, the general concerns are related to “blocking” legitimate applications, impacting business, and breaking workstations. With those concerns, I went through roughly 30,000 different IOC paths on which Red Canary has detected malicious, suspicious and unwanted software. The most common paths for malicious files to execute from include the following 5 locations:
- < drive letter >\users\appdata\local\temp
- < drive letter >\users\appdata\local
- < drive letter >\users\appdata
- < drive letter >\users\appdata\roaming
- < drive letter >\programdata
Applocker can also be specific to the file extension being blocked. In this case, I have highlighted the following extension types that should not execute out of the 5 locations above:
.ade, .adp, .ani, .bas, .bat, .chm, .cmd, .com, .cpl, .crt, .hlp, .ht, .hta, .inf, .ins, .isp, .jar, .job, .js, .jse, .lnk, .mda, .mdb, .mde, .mdz, .msc, .msi, .msp, .mst, .ocx, .pcd, .ps1, .reg, .scr, .sct, .shs, .svg, .url, .vb, .vbe, .vbs, .wbk, .wsc, .ws, .wsf, .wsh, .exe, .pif, .pub
I created and exported the Applocker policy and it is available to assist with preventing common and current threats in the common paths identified: https://github.com/MHaggis/hunt-detect-prevent/blob/master/Prevention/Applocker/applocker.xml

There are many extensions that may be blocked in the user profile and other paths. Gaining situational awareness across different departments and associates and then baselining what is normal/not normal will help prevent many things with Applocker.
2: Disable Macro execution with Microsoft Office Suite.
Reducing your attack surface by disabling macro execution is key to denying the majority of email-borne threats. By globally disabling macro execution within Microsoft Office and allowing for those who actually need macros, you will limit the scope of systems that can be compromised. As a backstop to disabling macros globally, Applocker can prevent malicious file types in the user profile.
Microsoft natively does not provide the ability to block macros, therefore you will need to download and import the ADMX files manually, then follow the steps provided in the guide. Office 2016 will natively come with macro execution blocked and GPO features built in.
- Download Office 2013 ADMX here: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=35554
- Enable configuration for blocking macros in GPO here: User Configuration/Administrative Templates/Microsoft Office XXX 20XX/Application Settings/Security/Trust Center/Trusted Locations
Blocking macros across an organization may seem daunting, but after gaining an understanding of who actually needs them, you can disable macros for the majority of your users and educate those who need them to be cautious of emails with suspicious attachments.
3: Screen Microsoft Windows files.
File screening can save your enterprise file server from having files overwritten during a ransomware infection. This is a short-term preventative control as ransomware is continuously changing the file extensions used. Generically, it’s a simple static stop gap that will require weekly updating in order to continue blocking the latest variants. Many sites exist today that provide the latest “malicious” extension used by ransomware, including the ransomware overview spreadsheet referenced above.
Additional areas to keep an eye on over time include ACLs on workstations and servers. For example, is the “Everyone” group needed? Locking down ACLs on critical shares is important to protecting critical data in any organization. Your final backstop on file servers are the actual backups performed daily, weekly, and monthly. It is critical that backups are stored offline and that you frequently test data restoration.
To get you started, here are two blog posts that assist with using File Screening and also provide a PowerShell script:
4: Take advantage of anti-ransomware tools.
Many security vendors are providing quick and easy solutions to easily thwart the mass encryption of systems. The idea behind these solutions is to place canary files on the file system and wait for it to be modified. I’ve seen success with these tools in preventing unknown variants of ransomware and I highly suggest you review them and find one that fits your organization.
Anti-ransomware tools
- https://ransomfree.cybereason.com/
- http://www.bitdefender.com/solutions/anti-ransomware-tool.html
- https://go.kaspersky.com/Anti-ransomware-tool.html
- https://forums.malwarebytes.com/topic/177751-introducing-malwarebytes-anti-ransomware-beta/
5: Educate your organization.
The single most valuable asset you have in the business is your Associates. They sit on the frontlines of spear-phishing attacks via email and phone calls, but one of the hardest problems to solve is securing the human element. I wish I could provide the easiest way to fix this, but like everything in Information Security – it is a journey, not a destination. The process I generally recommend is:
- Arm your associates: Educate with timely seasonal messages via email or office lunch and learns.
- Build a website: Provide up-to-date news (via RSS) on the latest phishing news from industry leaders.
- Lessons learned: Nefarious attempts should be used as a business lesson to all. Educate everyone when real-world attacks occur.
- Posters and newsletters: Post educational content around the organization, do monthly newsletters, and share important reminders on internal websites.
Many services exist today to provide you with a security awareness platform that includes training videos, template posters and newsletters, and simulated phishing exercises. Training the human element is one of the best preventative measures to add to any arsenal.
Key Takeaways
As defenders, we have to remember that ransomware is not the only problem we face; it is noisy, but only one part of the problem. No single product will shield your organization from ransomware. However, reviewing and utilizing the five countermeasures outlined above will get you on a path to reducing your attack surface. The ultimate goal is to make the attacker’s job hard. As new attack techniques are generated daily and weekly, detection becomes a primary source for monitoring and responding to all threat types. The key to understanding how much detection you need is understanding your prevention appetite. Good luck!
What countermeasures have you found to be effective? I’d love to hear your thoughts. Tweet me with questions, feedback, and new ideas.
For more tools and techniques from Michael Haag, watch the on-demand webinar: The Ransomware Epidemic: an End-to-End Look at the #1 Cyber Threat
 5 Countermeasures & Technical Controls
5 Countermeasures & Technical Controls