Highlights from March
For the first time, Amber Albatross is number 1 on our monthly top 10 most prevalent threat list. Amber Albatross is Red Canary’s name for a cluster of activity that starts from an adware program and leads to a pyInstaller EXE with stealer-like capabilities. We recently gained more insight into earlier stages of its execution chain. Being able to detect earlier stages of the activity gave us better visibility, which led to a higher volume of published threats for Amber Albatross in March and its place in the top spot.
Scarlet Goldfinch came in at number 2, the highest it has placed in our top 10 since its debut in September 2023. We observed a change in Scarlet Goldfinch’s fake update lures in March; along with more generic names like Update 7883.js, we saw lures target specific browsers, for example Chrome_231.23.05069.js or Firefox_71623.js. The most common payload we saw continued to be NetSupport Manager, which is why it made the list this month in a tie for 10th.
Our newcomer to the top 10 this month is Arechclient2, a remote access trojan (RAT) designed to steal sensitive information. It tied for 6th with HijackLoader—not a coincidence, since the activity chain we saw was paste and run followed by HijackLoader which delivered Arechclient2. We’ve seen Arechclient2 delivered by HijackLoader before, but not in the volume we observed last month. You can read more about Arechclient2 below.
This month’s top 10 threats
To track pervasiveness over time, we identify the number of unique customer environments in which we observed a given threat and compare it to what we’ve seen in previous months.
Here’s how the numbers shook out for March 2025:
| Month's rank | Threat name | Threat description |
|---|---|---|
| Month's rank: ⬆ 1 | Threat name: | Threat description : Red Canary-named cluster of activity that starts from an adware program and progresses through several stages to a pyInstaller EXE with stealer capabilities |
| Month's rank: ⬆ 2 | Threat name: | Threat description : Activity cluster that uses a distribution scheme similar to SocGholish and uses JScript files to drop NetSupport Manager onto victim systems |
| Month's rank: ⬆ 3 | Threat name: | Threat description : Collection of Python classes to construct/manipulate network protocols |
| Month's rank: ⬆ 3* | Threat name: | Threat description : Information stealer sold on underground forums and used by a variety of adversaries; may also be used as a loader for additional payloads |
| Month's rank: ⬇ 5 | Threat name: | Threat description : Red Canary's name for a VBS worm that is delivered via an infected USB and uses a printui DLL hijack to deliver a cryptomining payload |
| Month's rank: ⬆ 6* | Threat name: Arechclient2 | Threat description : Remote access tool (RAT) that also contains information stealer capabilities |
| Month's rank: ⬆ 6* | Threat name: | Threat description : Malware loader that uses DLL side-loading to deliver additional payloads through process injection |
| Month's rank: ⬆ 8* | Threat name: | Threat description : Activity cluster using a worm spread by external drives that leverages Windows Installer to download malicious files |
| Month's rank: ⬇ 8* | Threat name: | Threat description : Dropper/downloader that uses compromised WordPress sites to redirect users to adversary infrastructure posing as necessary browser updates to trick users into running malicious code |
| Month's rank: ⬇ 10* | Threat name: | Threat description : Open source tool that dumps credentials using various techniques |
| Month's rank: ⬇ 10* | Threat name: | Threat description : Legitimate remote access tool (RAT) that can be used as a trojan by adversaries to remotely control victim endpoints for unauthorized access |
⬆ = trending up from previous month
⬇= trending down from previous month
➡ = no change in rank from previous month
*Denotes a tie
HijackLoader delivers Arechclient2 via paste and run
In March 2025, Red Canary saw a wave of HijackLoader delivering Arechclient2, enough for Arechclient2 to make its debut in our top 10 list. Also known as SectopRAT, Arechclient2 is a remote access tool (RAT) that was first reported in November 2019. It’s notable for its capability to create a hidden secondary desktop interface, allowing operators to access the system at the same time as users. Arechclient2 also has stealer capabilities, targeting information like browser data and crypto wallets. In May 2024, Arechclient2 reportedly delivered Cobalt Strike and Brute Ratel as a precursor to BlackSuit ransomware deployment.
Arechclient2 is known for its capability to create a hidden secondary desktop interface, allowing operators to access the system at the same time as users.
Several loaders have delivered Arechclient2, including FakeBat, Amadey, and HijackLoader. Arechclient2 has a long history with HijackLoader; it was the delivered payload when HijackLoader (aka IDAT Loader, GHOSTPULSE, SHADOWLADDER) was first reported on in July 2023. Lures that kick off execution chains leading to Arechclient2 heavily leverage initial access techniques like malvertising, search engine optimization (SEO) poisoning, and typosquatting. Malicious ads trick users into navigating to adversary-designed sites that mimic legitimate software downloads including Google Chrome, Zoom, and NordVPN among others.
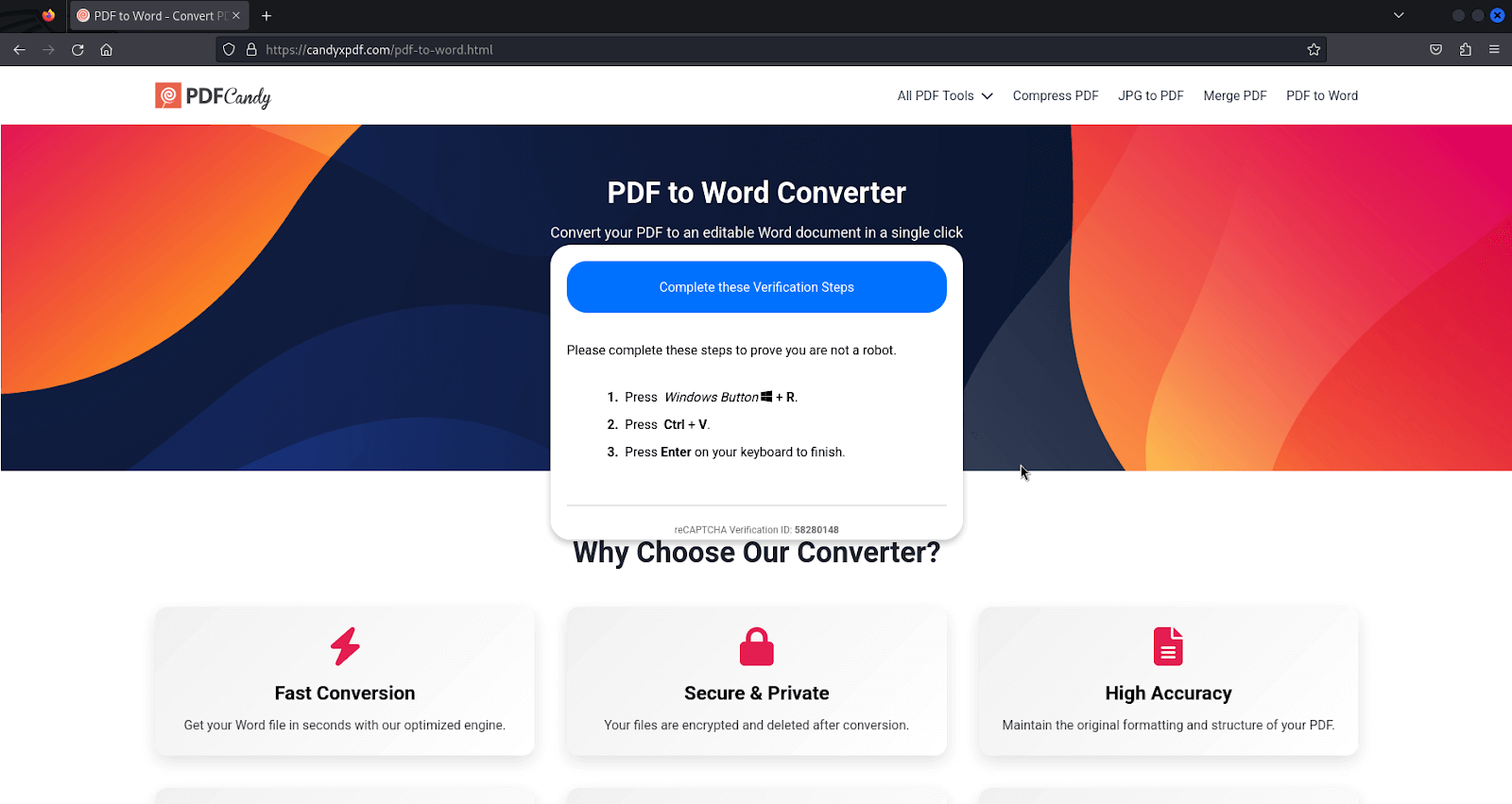
The activity we observed in March used paste and run (aka ClickFix, fake CAPTCHA) as the initial access vector. Based on public reporting that we assess is related to some of the activity we observed, operators registered domains and created a malicious website designed to impersonate the legitimate PDF converter PDFCandy. The paste and run command was included as part of the malicious website’s document conversion workflow.
Image from CloudSek
Here’s an example of one execution chain we observed:
Arechclient2 behavior to look out for
Suspicious behaviors by a cmd.exe-created process that Arechclient2 is injected into, for example msbuild.exe:
Netconns to pastebin[.]com, which Arechclient2 often uses to retrieve its command and control (C2) IP addresses:
Image from Elastic Security Labs
Arechclient2 frequently leverages atypical ports in its C2 communication; port numbers reported in OSINT include 15647, 15678, 15649, 15847, and 9000. In the Elastic example above, the configured TCP port was 15647.
Since Arechclient2 is typically a follow-on payload installed after initial access technique execution and loader activity, there are many detection opportunities available before Arechclient2 executes. For example, the activity we saw in March 2025 leveraged encoded PowerShell to make network communications, download resources, and execute files early in the execution chain. That gives us a detection opportunity.
Detection opportunity: Encoded PowerShell executing a command, establishing external network connections, and writing an executable to disk
The following pseudo-detection analytic looks for instances of powershell.exe executing an encoded command, establishing external network connections, and writing an executable to disk. These kinds of encoded commands are used by a number of threats, including paste and run leading to HijackLoader and Arechclient2, and are highly suspicious even without considering additional behavior like netconns and executable creation. Note that legitimate processes such as Chocolatey may use shortened -EncodedCommand flags.
process == (powershell.exe)
&&
deobfuscated_command_includes (' -e ', ' -ec ', ' -en ', ' -enc ', ' -enco ', ' -encod ', ' -encode ', ' -encoded ', ' -encodedc ', ' -encodedco ', ' -encodedcom ', ' -encodedcomm ', ' -encodedcomma ', ' -encodedcomman ')
&&
has_external_netconn
&&
file_creation_includes ('exe')


![Netconns to pastebin[.]com, which Arechclient2 often uses to retrieve its command and control (C2) IP addresses.](https://redcanary.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/pastebin.png)